Kitronik Unveils New Robotics Board for Raspberry Pi Pico
United Kingdom, Friday, 13 December 2024.
Kitronik’s latest robotics board for Raspberry Pi Pico drives 4 motors and 8 servos, enhancing robotics projects with versatile connectivity and power management. Released on 12 December 2024.
Advanced Features and Specifications
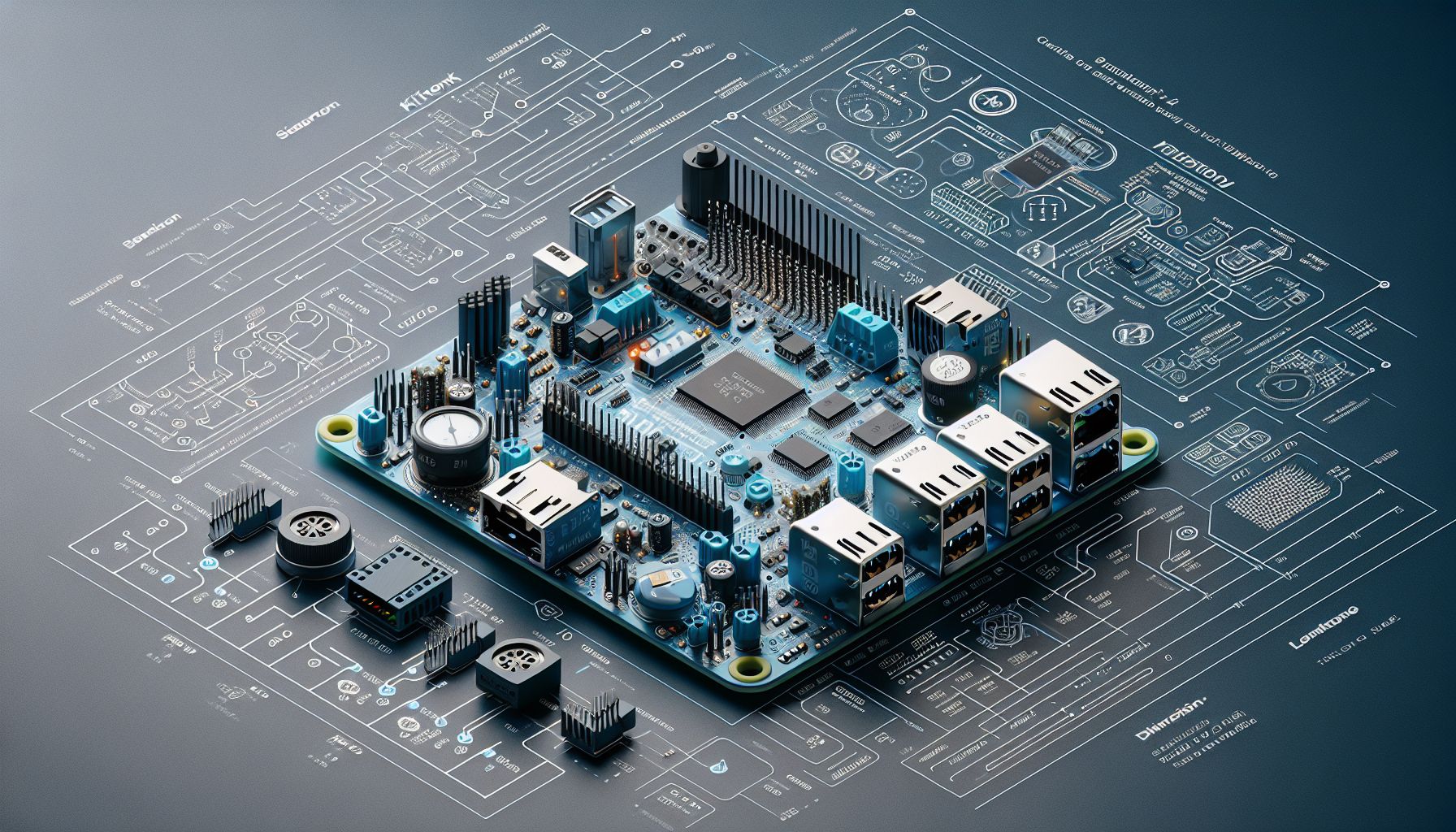
The new Kitronik Compact Robotics Board showcases impressive capabilities with 27 I/O expansion points and dual H Bridge Motor Driver ICs [1]. The board’s versatility is demonstrated through its ability to control either 4 DC motors or 2 stepper motors with half-stepping support, while simultaneously managing 8 servo motors [1]. Communication is handled via I2C protocol, utilizing a 16-channel driver IC for precise control [1]. With dimensions of 68 mm × 56 mm × 10 mm [1], this compact board efficiently maximizes space while delivering robust functionality.
Power Management and Connectivity
Power management features include a regulated 3.3V supply system with flexible input options through either a terminal block or servo-style connector [1]. The board incorporates an integrated power switch and status LED for easy monitoring [1]. However, users should note an important limitation: the board is not recommended for use with Raspberry Pi Pico W’s wireless functionality due to additional current draw considerations [1], which may affect project planning for wireless applications.
Market Position and Alternatives
In comparison to similar products like the Cytron Motion 2350 Pro, which offers 3A per channel and 3.6-16V operation [2], the Kitronik board positions itself as a more specialized solution for precision robotics projects. The robotics controller market currently includes various options, from educational kits to professional-grade solutions [4], with Kitronik’s offering standing out for its UK manufacturing credentials [1] and focus on integration with the popular Raspberry Pi Pico ecosystem.
Development Environment and Applications
The board supports MicroPython programming through the Thonny editor [1], aligning with current educational and development trends in the maker community [5]. This programming flexibility, combined with the board’s comprehensive feature set, makes it particularly suitable for both educational robotics projects and more complex mechatronic applications [1]. The board’s release comes at a time when MicroPython is gaining increasing adoption in educational and hobby electronics [5], providing a timely solution for the growing maker community.