Breakthrough in Microfluidic Manufacturing: IPFL's Innovative 3D Printing Technique
Cambridge, Thursday, 10 October 2024.
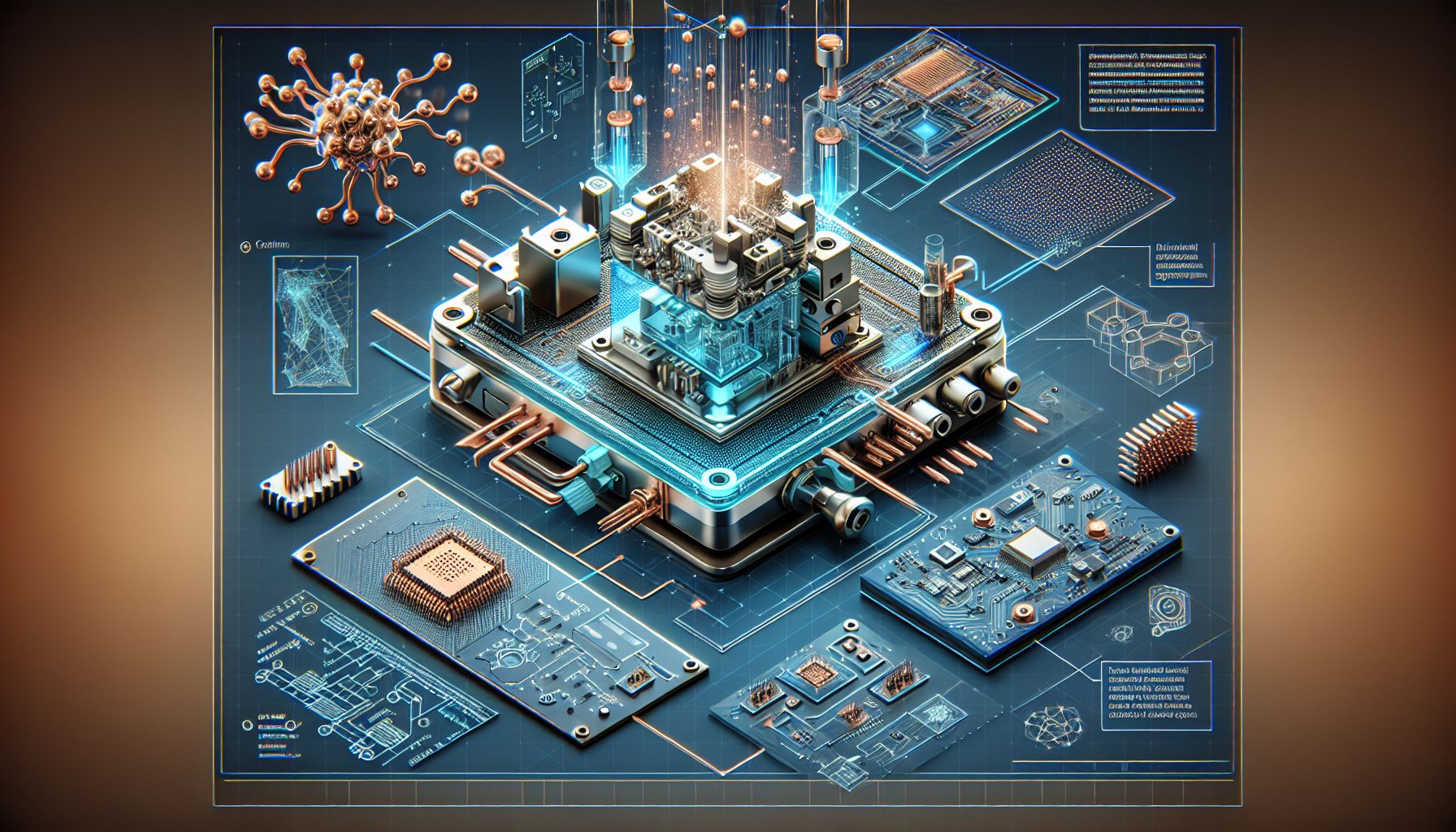
IPFL has developed a sophisticated component integrating embedded electronics within a microfluidic system using advanced micro 3D printing. This innovation, utilizing copper-infused BIO resin, showcases potential applications in medical diagnostics and lab-on-a-chip technology, pushing the boundaries of precision engineering.
Revolutionizing Microfluidics with Precision Engineering
In the fast-evolving landscape of microfluidics, IPFL’s recent advancements mark a significant leap forward. By employing Boston Micro Fabrication’s (BMF) cutting-edge 3D printing systems, IPFL has successfully manufactured a microfluidic component that bridges two bioreactors. This intricate connector, crafted with copper-infused BIO resin, not only enhances conductivity but also fortifies mechanical strength, crucial for high-performance applications in medical diagnostics and lab-on-a-chip technologies[1].
The Role of Advanced 3D Printing Technologies
The micro 3D printing technology leveraged by IPFL employs BMF’s Projection Micro-Stereolithography (PμSL), which enables the production of components with 10µm and 2µm resolution. This precision is unmatched in traditional manufacturing methods, allowing IPFL to meet the stringent requirements of the microfluidic environment. As Michael Herda from Pristine Surgical noted, such technology facilitates rapid prototyping and iteration, accelerating product development cycles while maintaining high standards of quality and detail[2].
Potential Applications and Industry Impact
The integration of embedded electronics within microfluidic systems signifies a major advancement, particularly in fields requiring precise fluid manipulation and sensor integration. This innovation opens doors to new possibilities in medical diagnostics, enabling more accurate and efficient testing and analysis. Furthermore, the ability to create complex, high-precision components is expected to drive future developments in bioengineering and precision medicine, as evidenced by recent research into micro 3D printing for drug delivery systems[3].
Expert Insights and Future Directions
Experts from the Microsystems Laboratory at EPFL emphasize the transformative potential of integrating electronics into microfluidic systems. By embedding electronic components directly during the manufacturing process, it is possible to achieve unprecedented levels of functionality and integration. This aligns with global trends in 3D printing, where additive manufacturing is increasingly used to overcome the limitations of traditional production methods[4]. As the industry moves forward, continued innovation in materials and printing techniques will be key to unlocking further advancements in microfluidics and related fields.